https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/https://www.rawpixel.com/image/9975831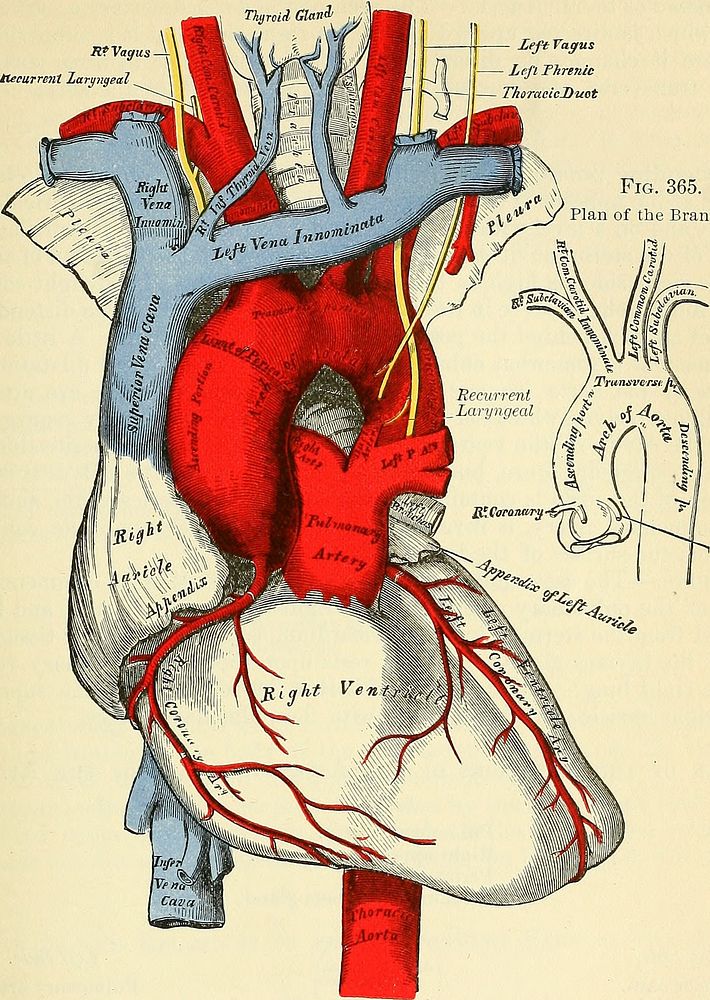

Identifier: anatomydescripti1887gray (find matches)Title: Anatomy, descriptive and surgicalYear: 1887 (1880s)Authors: Gray, Henry, 1825-1861 Pick, T. Pickering (Thomas Pickering), 1841-1919, ed Keen, William W. (William Williams), b. 1837Subjects: Human anatomy AnatomyPublisher: Philadelphia : Lea brothers & co.Contributing Library: Francis A. Countway Library of MedicineDigitizing Sponsor: Open Knowledge Commons and Harvard Medical SchoolView Book Page: Book ViewerAbout This Book: Catalog EntryView All Images: All Images From BookClick here to view book online to see this illustration in context in a browseable online version of this book.Text Appearing Before Image:o branches for the two lobes. The terminal branches of the pulmonary artery will be described with theanatomy of the Lung. The Aorta. The Aorta (dopry, arteria magna) is the main trunk of a series of vessels which,arising from the heart, convey the red oxygenated blood to every part of the bodyfor its nutrition. This vessel commences at the upper part of the left ventricle, and,after ascending for a short distance, arches backward and to the left side over theroot of the left lung, descends within the thorax on the left side of the vertebralcolumn, passes through the aortic opening in the Diaphragm, and, entering theabdominal cavity, terminates, considerably diminished in size, opposite the fourth THE AORTA. 503 lumbar vertebra, where it divides into the right and left common iliac arteries.Hence its subdivision, from the direction or position of its parts, into the arch of Fig. 364. SfVagus -i ttecurrent laryngeal Left Vagus ; Left Threnic TkoracicDuot Fig. 365. Plan of the Branches.Text Appearing After Image:\Left Coronary The Arch of the Aorta and its Branches. the aorta, (and) the descending (aorta, which last is again divided into the) thoracieaorta and the abdominal aorta.1 Arch of the Aorta. Dissection.—In order to examine the arch of the aorta, open the thorax by dividing the car-tilages of the ribs on each side of the sternum, raising this bone from below upward, and thensawing through the sternum on a level with its articulation with the clavicle. By this meansthe relations of the large vessels to the upper border of the sternum and root of the neck are keptin view. The Arch of the Aorta extends from the origin of the vessel at the upper partof the left ventricle to the lower border of the body of the fifth dorsal vertebra.At its commencement it ascends behind the sternum obliquely upward and forwardtoward the right side, and opposite the upper border of the second costal cartilage 1 These portions of the aorta would be better named transverse aorta, dorsal aorta, and abdominaloNote About ImagesPlease note that these images are extracted from scanned page images that may have been digitally enhanced for readability - coloration and appearance of these illustrations may not perfectly resemble the original work.
Original public domain image from Wikimedia Commons
Public DomainFree CC0 image for Personal and Business use